Do you know the difference between Tesla's braking system and traditional cars? How does AP assisted driving control the brakes?
Let me briefly introduce
This is the brake master cylinder, the white is the reservoir (storage brake fluid), there is a piston inside the cylinder, and the two holes next to it are the oil inlet and outlet holes
Here's how it works:
When the brake pedal is stepped on, the brake lever will apply a thrust to the brake master cylinder, and the piston in the cylinder will open the oil outlet after being pressured, and the brake oil in the white reservoir will flow out from the two oil holes. The brake oil pipe flows to the brake cylinder of each wheel. After the piston inside the cylinder is subjected to hydraulic pressure, it pushes the brake pads and hugs the brake disc to complete the brake through friction. When the brake pedal is released, the brake master cylinder The oil outlet hole in the engine is closed, the oil inlet hole is opened, and the brake oil flows from each brake cylinder to the brake master cylinder, returning to the original state
Video analysis (from YouTube blogger Autodata Training)
A: In this case, it is very labor-intensive to brake the four wheels by means of hydraulic brakes and mechanical brakes. Is there a more labor-saving way?
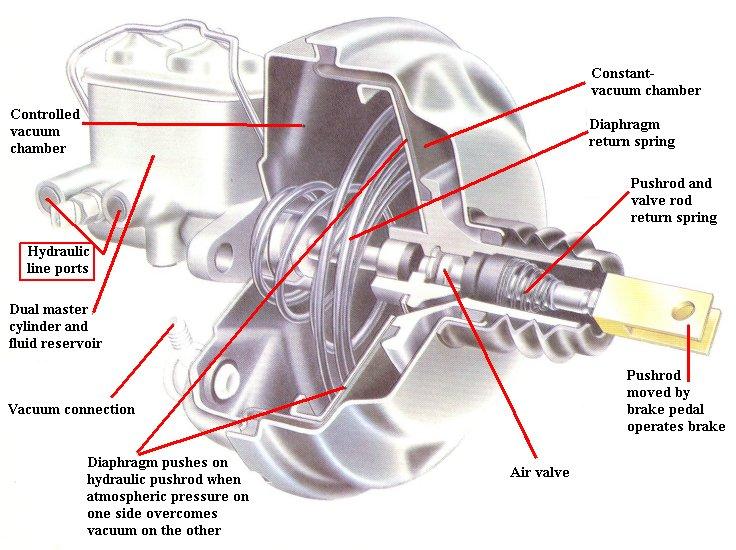
Q: Yes, in traditional cars, the brake master cylinder is not directly connected to the brake pedal push rod, and there is still a very important role between them, that is, the "vacuum booster pump"
Specifically, in the big black disc of the vacuum booster pump, there is a chamber divided into a left chamber and a right chamber by a diaphragm in the middle. The vacuum booster pump is connected to the intake manifold of the engine. After the engine starts, it will pass The pipeline pumps out the air in the chamber to form a vacuum state. When the brake pedal is stepped on, the engine generates air pressure and enters the channel in the middle of the booster pump. Under the action of the push rod, the vacuum valve is closed, the air valve is opened, and the air enters the right side. Chamber, because the air pressure is greater than the vacuum pressure, so under the action of negative pressure, the diaphragm will move to the left
, form a joint force with the braking force of the driver's foot, and use the boost of the pressure difference to make the braking easier
Video analysis (from YouTube blogger Thomas Schwenke)
But Tesla doesn't have an engine, and he uses the second-generation IBooster electromechanical brake booster, so what is its working principle?
Pry the shell open, inside it is a motor and a set of purely mechanical gear structure, the end with the push rod is connected to the brake pedal, and the other end is connected to the brake master cylinder

The metal screw rod in the middle is responsible for driving the brake master cylinder. This black sensor is used to measure the force when you step on the brake, and transmit the brake signal to the ECU, and then the ECU orders the motor mentioned above to start working to drive These reduction gears rotate, so that the metal screw rod will push outward, and then push to the brake master cylinder. When the pedal is pressed, the screw will be reset by the spring. The reason why the AP assisted driving can automatically brake is because the ECU can control the brake motor alone to work.

Video analysis (from YouTube blogger SuperfastMatt)

